

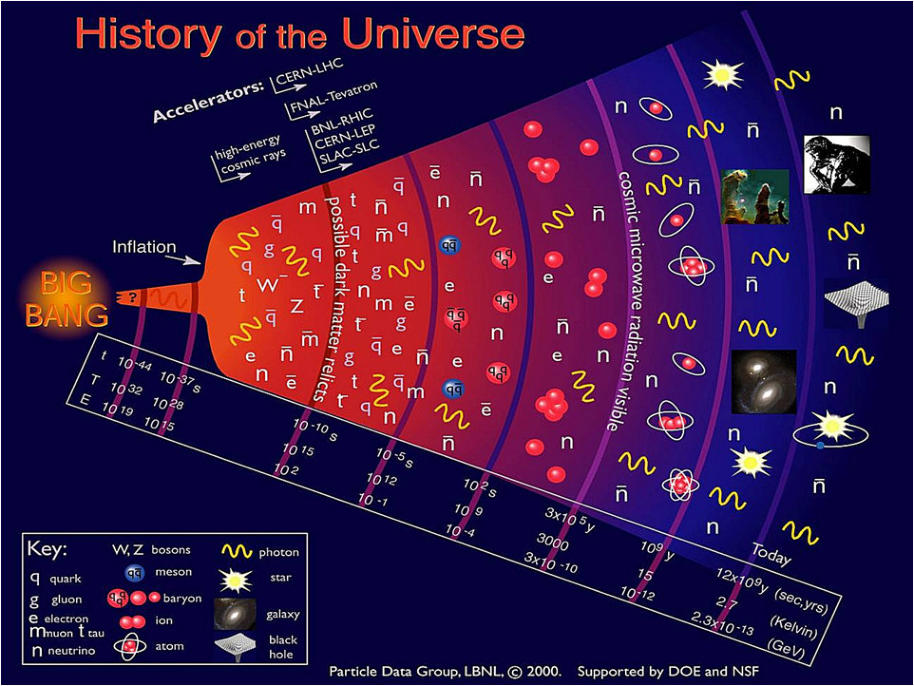
Thanks to particle colliders, we began to understand the fundamental
matter that makes up the universe. Particles combine to form new
particles grouped into families: Fermions, Bosons, Quarks, Hadrons,
Mesons, etc., all with their corresponding antiparticle.
In the approximately, 13.8 billion years the universe is estimated to
have, we can observe a particle: the photon, which has remained as
a energy carriage since the beginning. This energy field, as it
interacts with different particles in our environment, can transform
and, under certain processes, convert into matter — photon to
electron and usable mass — though that direct conversion is more
complex and depends on specific conditions.


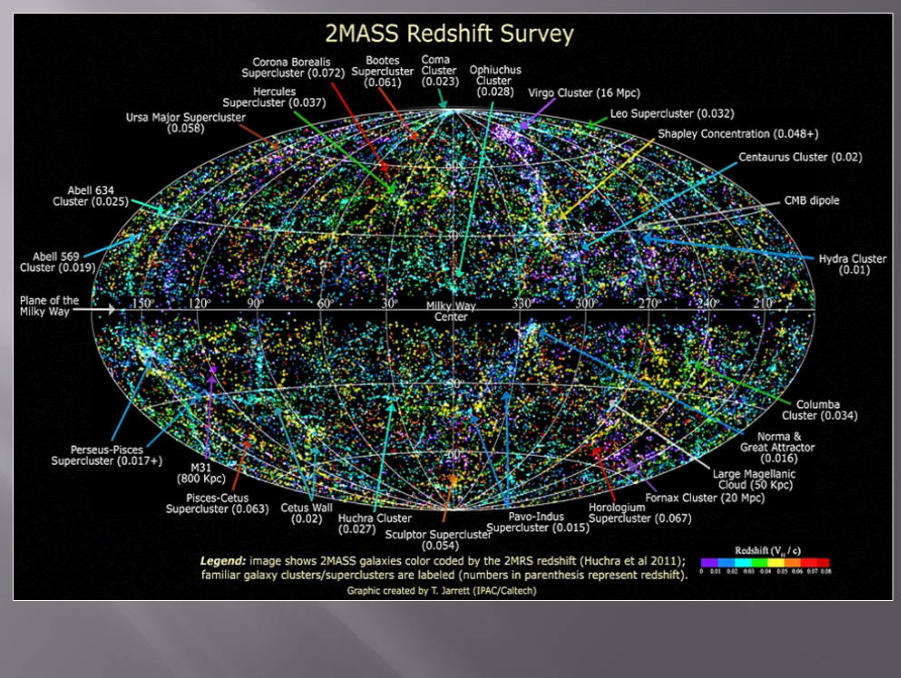
CURRENLY

Current map of our universe: it is estimated that there are between
100 and 200 billion galaxies, and between 100 and 1000 billion stars
per galaxy. Although the Milky Way is located at the center, that does
not mean we are the center of the universe; it is where the 2MASS
telescope scanned from. The different colors reflect the Doppler
effect: galaxies moving away from us appear red, while those
approaching are blue.
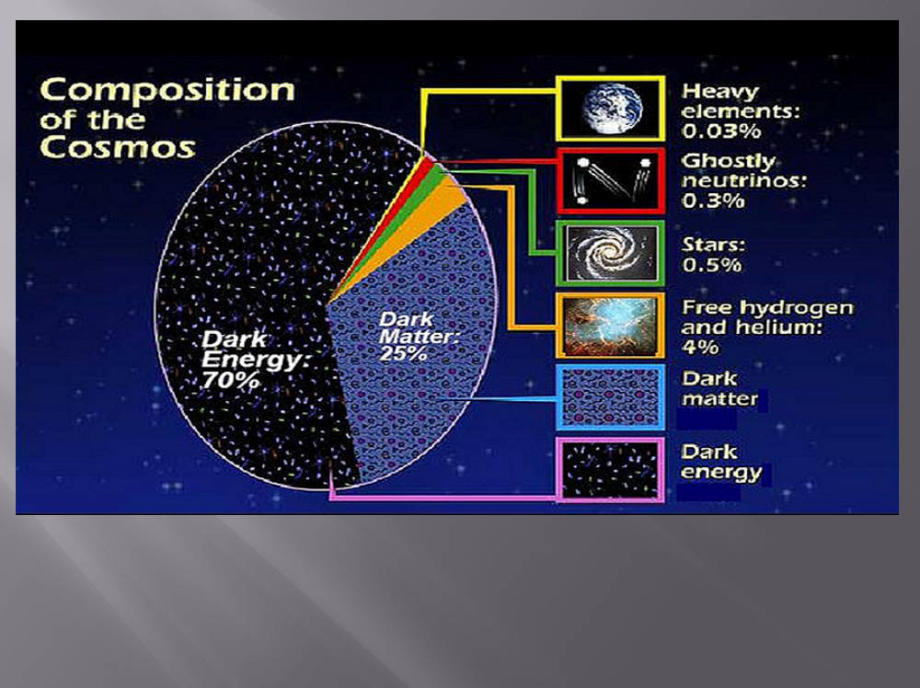
All the particles that make up the universe have their corresponding
antiparticle. Practically we only know about 5% of its composition.
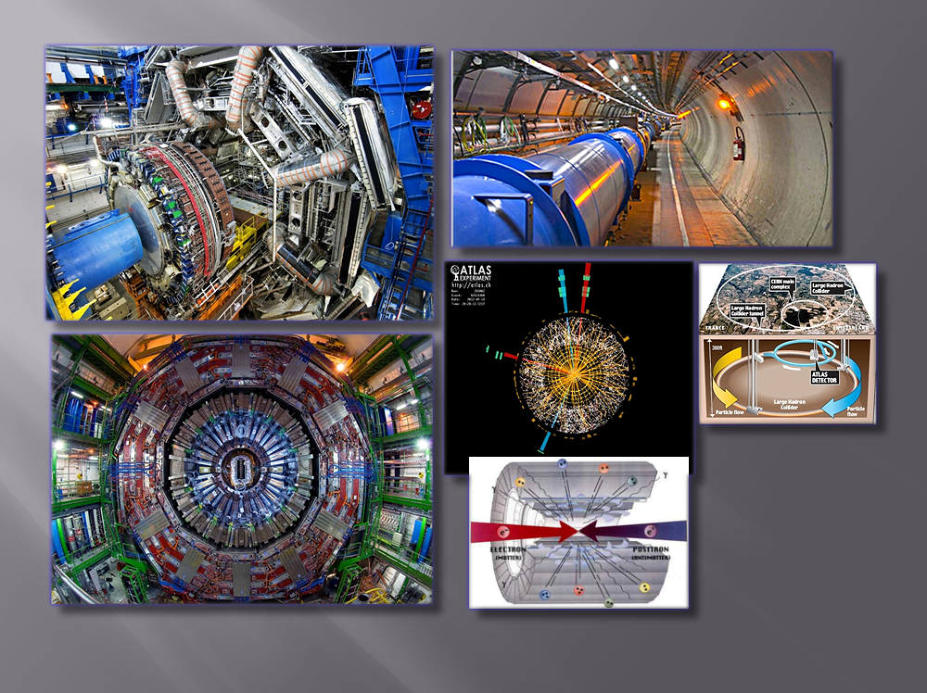
LHC
The Hadron Collider, located between Switzerland and France, is a 27 km tunnel
with a circumference, buried between 50 and 175 meters, composed of 1,650
superconducting magnets at -271 °C. The ATLAS particle detector is over 50 meters tall.
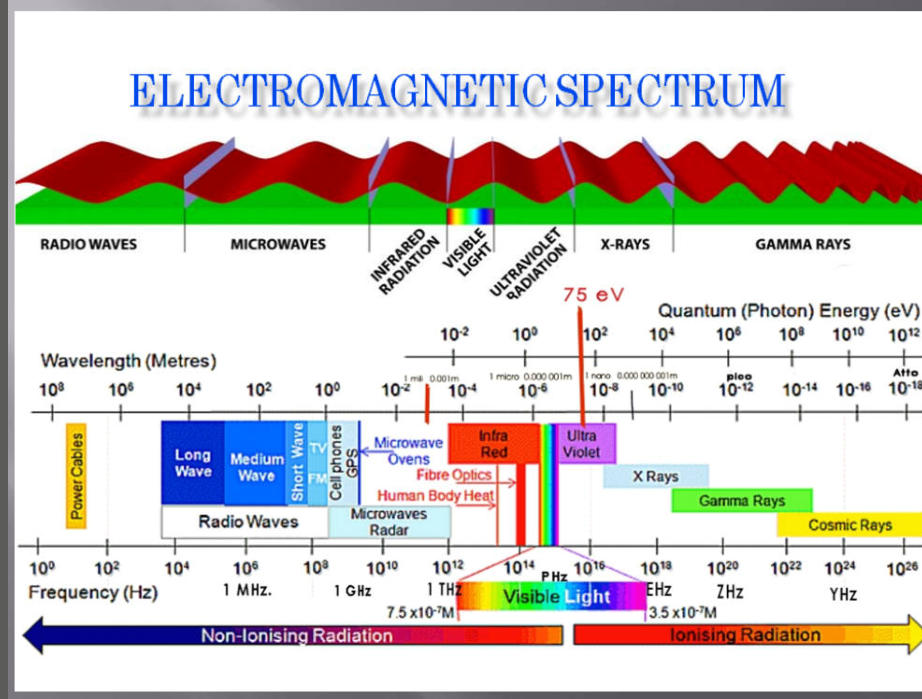
In this diagram we can observe the different uses that this small
energy carrier provides us. We are only able to detect its effects,
organized, and the rest with suitable measuring devices in small
radiation sectors. In the infrared we notice heat; the radiation part
marked as visible we can see because its wavelength in this sector is
the same as the detectors in our eyes. In ultraviolet it allows us to go
from tanned skin to skin damaged by excessive exposure to this
radiation, and in X-rays, Gamma rays, and cosmic rays, we find that
its energy is still too high, destroying our cells when it impacts them.

RVM

Previous
Following


















